Fossil Ginkgophyta are one of the most widely used indicators for estimating the paleoatmospheric CO2 levels from the Triassic to present day. There are quite a few CO2 estimates for the Triassic to Jurassic interval; however, the data from China are still limited. Recently, Dr. WU Jingyu, Post Doc of NIGPAS and associate Professor of Lanzhou University, in collaboration with Prof. WANG Yongdong in NIGPAS, have investigated two fossil Ginkgoites species, G. magnifolius Du Toit and G. obrutschewii (Seward) Seward from collections from the Upper Triassic and Middle Jurassic in Huating County, Gansu Province, Northwest China. The fossil leaf morphology and epidermal structure were studied and the stomatal parameters were analyzed for the reconstruction of paleoatmospheric CO2 concentrations. The results were recently published in the international “Paläontologische Zeitschrift” published in Germany.
The paleoatmospheric CO2 levels during the Late Triassic of China is estimated for the first time based on fossil material from Gansu. This study demonstrates that fossils yield paleo-CO2 values of 1962 ppmv in the Late Triassic and 1320 ppmv in the Middle Jurassic. Compared with previous estimates of atmospheric CO2 concentration based on stomatal parameter of fossil Ginkgo/Ginkgoites from Northwest China, the change of Jurassic paleo-CO2 levels accord with the trend of CO2 concentration proposed by GEOCARB III and Crustal Production models. The results demonstrate that the paleo-CO2 of the Late Triassic was higher than that of the Early to Middle Jurassic; but an increasing trend of paleo-CO2 could be detected from the Early to the Middle Jurassic. The present data provide an independent check for the paleo-CO2 value estimation based on isotopic analysis. This represents the follow up study results by Wang Yongdong’s research team in recent years after significant results were get published in Earth-Science Reviews on Cretaceous palaeo-CO2 variation and greenhouse climate.
Information of publication: Wu Jing-yu, Ding Su-ting, Li Qi-jia, Sun Bai-nian, Wang Yong-dong*, 2016. Reconstructing paleoatmospheric CO2levels based on fossil Ginkgoites from the Upper Triassic and Middle Jurassic in Northwest China.Paläontologische Zeitschrift, Doi: 10.1007/s12542-016-0300-1.
Cuticles and stomata of fossil leaves of Ginkgoites
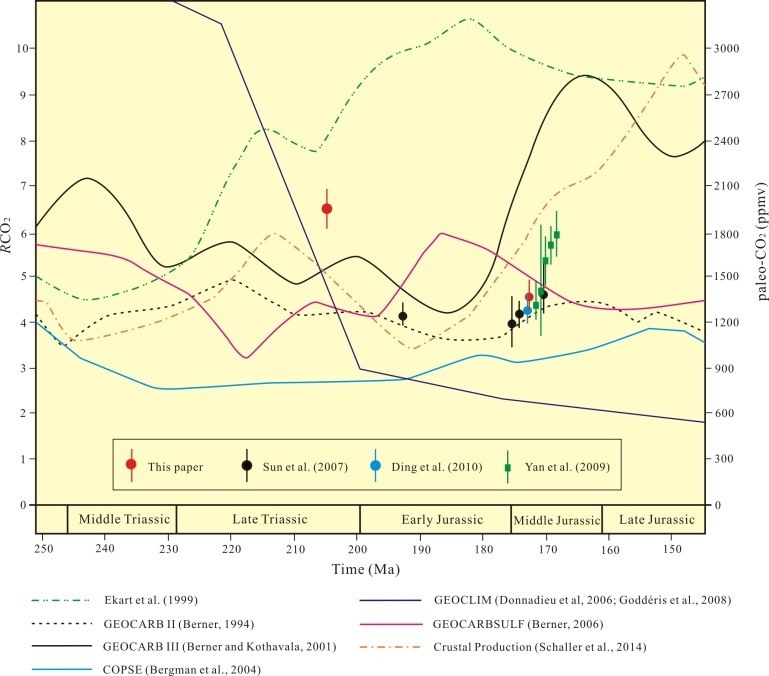
Paleo-CO2 variations during the Late Triassic to the Middle Jurassic based on the stomatal ratios of Chinese plant fossils, and comparison with geochemical models
