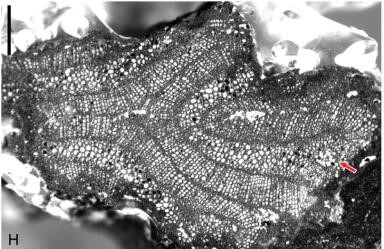
Transverse section of fern-like plant Shougangia stem from the Upper Devonian of China
A further study on the anatomy of Shougangia bella from the Late Devonian (Famennian) of South China is carried on the workgroup of Prof. XU Honghe from Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. Wang Deming from Peking University. The study release the anatomy feature of Shougangia and provide a reconstruction based on its known morphology, which was studied by them previously.
Shougangia stems contain a dissected stele with a four-ribbed and an elongatecurved primary xylem segments changing to three elongate and slightly curved segments. Primary branches have a dissected stele with three similar primary xylem segments as in stems. The primary xylem of the stems and primary branches is mesarch, and individual primary xylem segments bear peripheral protoxylem strands and are surrounded by secondary xylem. Shougangia is anatomically compared with fern-like plants, zygopterid ferns and early seed plants, verifying its uncertain affinity at class and order levels as suggested by morphology, or representing a new order within the Cladoxylopsida. By the Late Devonian, besides the abrupt drop of atmospheric CO2 levels, the presence of secondary xylem may correlate well with the primary radiation of leaves (megaphylls) of euphyllophytes (e.g. fern-like plants, sphenopsids, progymnosperms and seed plants).
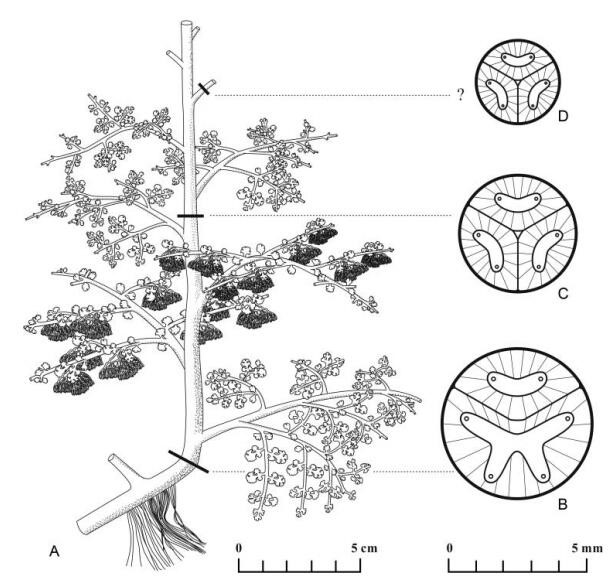
Reconstruction of morphology (A) and anatomy (B–D) of the Late Devonian fern-like plant Shougangia from China
Download:
