Well-developed Devonian deposits are widely spread in west and east marginal areas of the Junggar Basin, North Xinjiang, which acts are representative areas of Devonian flora of North China. The Devonian strata of the eastern and western sides of the Junggar Basin belong to different palaeoblocks paleogeographically, and scholars have been conducting more in-depth studies on plant fossils of the West Jungga.However, few knowledge of plant fossils from the Devonian of East Junggar hinders understanding to its flora and further comparison. Hence, it is necessary to carry on stratigraphical and palaeotological study to the Devonian of East Junggar, for the significances of early land plant evolution and palaeogeography.
Recently, the Devonian Investigation Group (DIG) of Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS), led by Prof. XU Honghe, conducted a systematic palaeontological study based on materials from the Upper Devonian of East Junggar, Fuyun, Xinjiang. The related research results were published online in the international journal Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology.
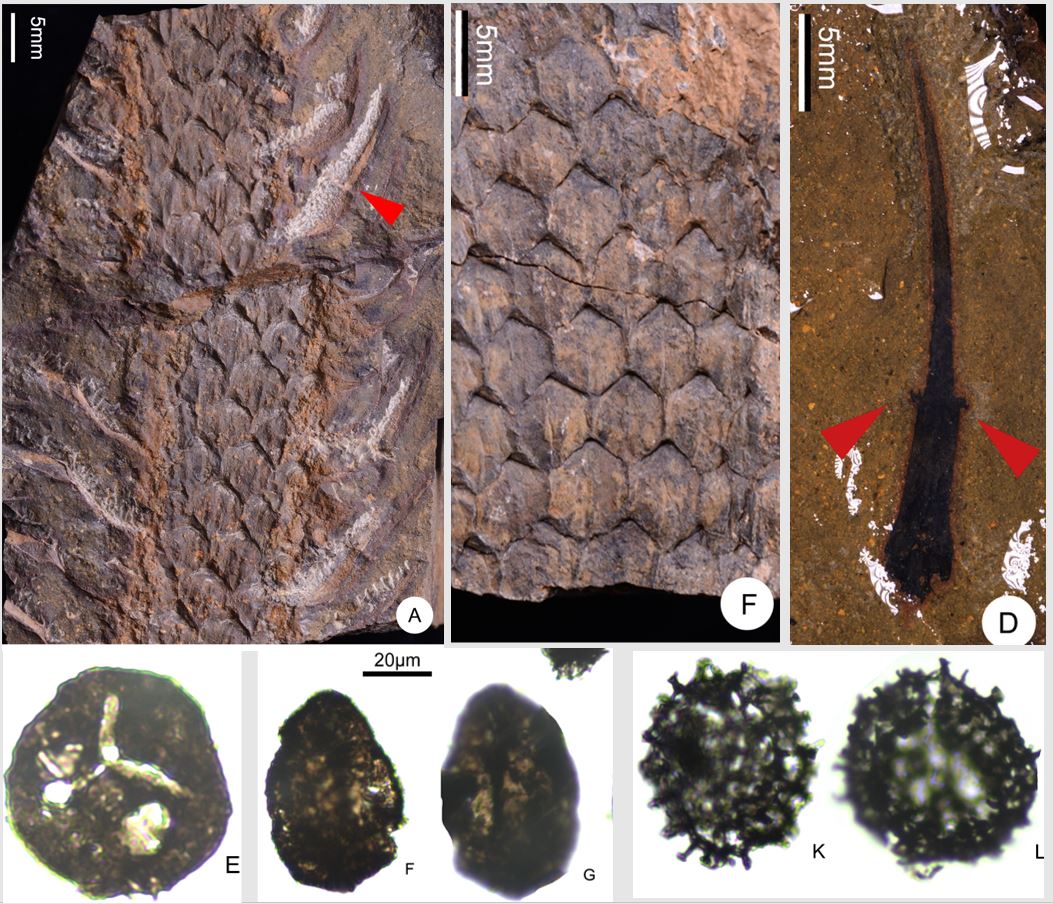
In this study, the lycopsid Gilboaphyton (Protolepidodendrales) is discovered as a new species. Gilboaphyton fuyunensis, which is characterized by pseudo-spirally longitudinal–hexagonal to fusiform leaf base, slender and entirely marginal leaf with two lateral up turned segments occurring at its one third portion from the base. Using palynological result the study dated and correlated the plant fossil-bearing strata.
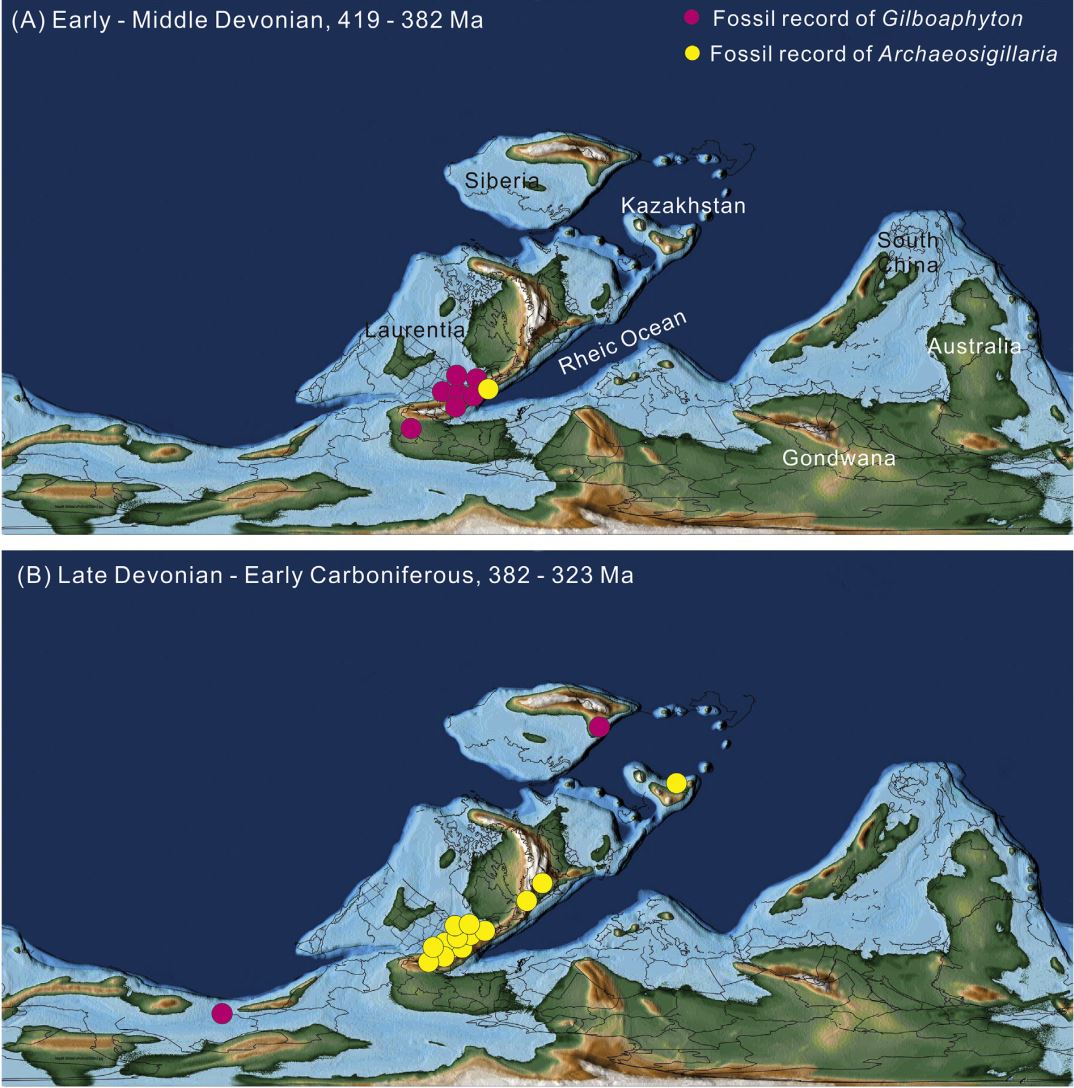
The research also visualized the spatio-temporal distribution pattern of Gilboaphyton base on its global occurrence data. It is suggested that Gilboaphyton was probably originated in southeastern Laurentia in the Early-Middle Devonian, and spread to the Siberia and Gondwana blocks towards northeast and southwest respectively in the Late Devonian to Early Carboniferous. The similar spatio-temporal distribution of Gilboaphyton and Archaeosigillaria suggest that the two genera might belong to the same plant.
Reference: Bing-Cai Liu, Jiao Bai, Yao Wang, Ning Yang, Hong-He Xu *, 2021. On the discovery of Gilboaphyton (Lycopsida) from the Upper Devonian of East Junggar, Xinjiang, and its global distribution. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology. 292, 104473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.revpalbo.2021.104473.
Fig 1. Fieldwork photo of Devonian investigation Group NIGP-CAS fieldwork in East Junggar, Xinjiang Fig 2. Gilboaphyton fuyunensis Liu et Xu and spores from the Upper Devonian Kaxiweng Formation, Fuyun, Xinjiang, China. Fig 3. Occurrences of Gilboaphyton (pink disks) and Archaeosigillaria (yellow disks) species plotted on the Early-Middle Devonian (A) and Late Devonian–Early Carboniferous (B) palaeogeographic maps.

Download:
